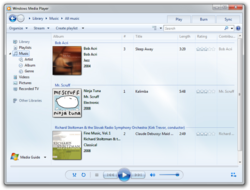
Windows Media Player
Windows Media Player A component of Microsoft Windows |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Details | |
| Type | Media Player Application |
| Included with | Windows Me Windows 2000 Windows XP[1] Windows Server 2003 Windows Vista[1] Windows Server 2008 Windows 7[2] |
| Replaces | Media Player |
Windows Media Player (abbreviated WMP) is a proprietary digital media player and media library application developed by Microsoft that is used for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as on Pocket PC and Windows Mobile-based devices. Editions of Windows Media Player were also released for Mac OS, Mac OS X and Solaris but development of these has since been discontinued.
In addition to being a media player, Windows Media Player includes the ability to rip music from and copy music to compact discs, burn recordable discs in Audio CD format or as data discs with playlists such as an MP3 CD, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and enable users to purchase or rent music from a number of online music stores.
Windows Media Player replaced an earlier application called Media Player, adding features beyond simple video or audio playback.
Windows Media Player 12 is the most recent version of Windows Media Player as of July 2009. It was released in July 22, 2009 [3] along with Windows 7 and has not been released for previous versions of Windows.[4]
Windows Media Player 11 is available for Windows XP and included in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. The default file formats are Windows Media Video (WMV), Windows Media Audio (WMA), and Advanced Systems Format (ASF), and supports its own XML based playlist format called Windows Playlist (WPL). The player is also able to utilize a digital rights management service in the form of Windows Media DRM.
Contents |
History

Microsoft Windows has had a media player since 1991, when Windows 3.0 with MultiMedia Extensions was released.[5] This version of Windows, which was included with "Multimedia PC"-compatible machines but not available for retail sale, included the Media Player application, was capable of playing .mmm animation files, and could be extended to support other formats.[6] It used MCI to handle media files. In November of the following year, Video for Windows was introduced with the ability to play digital video files in an AVI container format,[7] with codec support for RLE and Video1, and support for playing uncompressed files. Indeo 3.2 was added in a later release. Video for Windows was first available as a free add-on to Windows 3.1, and later integrated into Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0.
In 1996 Microsoft released ActiveMovie, a replacement for Video for Windows that incorporates a new way of dealing with media files, and adds support for streaming media (which the original Media Player couldn't handle).[8]
ActiveMovie was renamed to DirectShow in 1996,[9] and a new Media Player was created, known internally as Media Player 2.
All versions branded Windows Media Player (instead of simply Media Player) support DirectShow codecs. Version 6.4 was included with Windows Me, Windows 2000 and Windows XP, but was dropped in Windows Vista. Windows Media Player version 7 was a large revamp, first included with Windows Me with a new user interface, visualizations and increased functionality.
Beginning with Windows Vista, Windows Media Player supports the Media Foundation framework besides DirectShow; as such it plays certain types of media using Media Foundation as well as some types of media using DirectShow.[10]
Features
- Allows the user to connect, share and sync data with portable handheld devices and game consoles since version 7. Media can be optionally transcoded to a format better suited for the target device, automatically, when synchronizing. When deleting playlists from devices, Windows Media Player can automatically remove their contents. Devices can be formatted using Windows Media Player 9 Series and later. Version 10 and later support the Media Transfer Protocol and Auto Sync. Auto Sync allows users to specify criteria such as recently added music or highest rated songs, by which media will be automatically synchronized with the portable device and other advanced features like setting the clock on the portable device automatically, communicating with the device to retrieve the user's preferences. Windows Media Player 10 also introduced the UMDF-based Windows Portable Devices API.
- Playback of audio, video and pictures, along with fast forward, reverse, file markers (if present) and variable playback speed (seek & time compression/dilation introduced in WMP 9 Series). Items in a playlist can be skipped over at playback time without removing them from the playlist.
- Supports local playback, streaming playback with multicast streams and progressive downloads.
- Support for any media codec and container format using specific DirectShow filters or Media Foundation codecs (Media Foundation codecs only in Windows Vista and later).
- Full media management, via the integrated media library introduced first in version 7, which offers cataloguing and searching of media and viewing media metadata. Media can be arranged according to album, artist, genre, date et al.. WMP 9 Series introduced ratings and Auto Ratings. Windows Media Player 10 introduced support for aggregating pictures, Recorded TV shows, and other media into the library. Windows Media Player 12 drops the integrated library for Windows 7's libraries.
- Windows Media Player 9 Series introduced Quick Access Panel to browse and navigate the entire library through a menu. The Quick Access Panel was also added to the mini mode in version 10 but was entirely removed in version 11.
- Video Smoothing introduced in WMP 9 Series (Windows XP and later only) which upscales frame-rate by interpolating added frames, in effect giving a smoother playback on low-framerate videos.
- Includes a 10-band graphic equalizer with presets and SRS WOW audio post-processing system. Windows Media Player can also have attached audio and video DSP plug-ins which process the output audio or video data.
- Features a taskbar-mounted Mini mode in which the most common media control buttons are presented as a toolbar on the Windows taskbar. Flyout windows can display media information, the active visualization or the video being played back. Mini-mode was introduced as a shell player powertoy for Windows Media Player 8 in Windows XP and integrated later into WMP 9 Series. Mini-mode has been removed in Windows Media Player 12 in favor of controls in the taskbar's interactive thumbnail preview which lacks volume control, a progress bar and information displayed whenever a new song is played.
- Can use video overlays or VMR (Video Mixing Renderer) surfaces, if the video card supports them. In Windows XP, it uses VMR7 by default, but can also be made to use the more advanced YUV mixing mode by enabling the "Use high quality mode" option in Advanced Performance settings. This turns on deinterlacing, scaling and improved color accuracy.[11] WMP 9 Series introduced native playback for deinterlacing for TV output.
- Version 9 introduced DXVA accelerated playback. Version 11 introduced improved support for DirectX accelerated decoding of WMV video (DXVA decoding)
- Features integrated Audio CD-burning support since version 7 as well as data CD burning support since Windows Media Player 9 Series on Windows XP and later. Data CDs can have any of the media formats supported by the player. While burning Data CDs, the media can, optionally, be transcoded into WMA format and playlists can be added to the CD as well. Starting with WMP 9 Series, audio CDs can be burnt with volume leveling.
- Audio CDs can be ripped as WMA or WMA 10 Pro (WMA 10 Pro in WMP 11 and later) at 48, 64, 96, 128, 160 and 192 kbit/s, WMA lossless (470 to 940 kbit/s) (9 Series on XP and later), WMA variable bitrate (from 40-75 kbit/s up to 240-355 kbit/s), MP3 at 128, 192, 256 and 320 kbit/s, or uncompressed WAV (WAV ripping in WMP 11 and later). Since WMP 9 Series, 24 bit high-resolution CDs (HDCDs) are also supported, if capable audio hardware is present. Audio can be ripped using error correction and ripped audio can be protected with Windows Media DRM. Ripping to MP3 is supported only in Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP and later if a compatible MP3 encoder is installed. Windows Media Player 10 included the Fraunhofer MP3 Professional encoder.
- Information on CDs such as album name, artist and track listings can optionally be automatically downloaded from the online Windows Media database when the CD is inserted.
- Includes intrinsic support for Windows Media Audio Professional codec on Windows XP with WMP 9 Series and later which supports multichannel audio at up to 24-bit 192 kHz resolution.
- Can play files in WMA, WAV or MP3 media formats. However, it will not play MP3 files that contain compressed ID3 headers ("tags"); trying to do so results in a "The input media file is invalid" error message. MP3 playback support was built-in beginning with version 6.1 and audio CD playback was natively supported with version 7.
- Supports subtitles and closed-captioning for local media, video on demand streaming or live streaming scenarios. Typically Windows Media captions support the SAMI file format but can also carry embedded closed caption data.
- Windows Explorer shell integration to add files and playlist to the Now Playing pane and other playlists can be controlled from the Windows Explorer shell itself, via right-click menu. The My Music folder also includes a separate My Playlists folder where playlists are maintained. When the player is closed and reopened, simply clicking the play button restores the last playlist even if it was not saved. Starting with Windows Media Player 10, the playlist pane is also visible from the Library view. AutoPlay handlers in Windows expose various Windows Media Player tasks.
- Provides an embeddedable ActiveX control for Internet Explorer so that developers can play Windows Media on web pages.
- A fully featured tag editor was featured in versions 9-11 of WMP, called the Advanced Tag Editor. However, the feature was removed in Windows Media Player 12.
- Features static lyrics and "Synchronized Lyrics", by which different lines of lyrics can be time-stamped, so that they display only at those times. Synchronized Lyrics also were accessible through the Advanced Tag Editor.
- Has skinning support since version 7 and includes a color chooser since version 8. Not all functions are usually exposed in skin mode. Windows Media Player 10 allows setting the video border color. Color chooser has been removed in Windows Media Player 12.
- Since WMP 9 Series, the player features dynamically updated Auto Playlists based on criteria. Auto Playlists are updated every time users open them. WMP 9 Series and later also supports Auto Ratings which automatically assigns ratings based on the number of times a song is played. Pre-populated auto playlists are included in Windows Media Player 9 Series. Custom Auto Playlists can only be created on Windows XP and later.
- Includes Background plug-in, window plug-in and Now Playing plug-in support to control media playback besides DSP and renderer plug-ins. Plug-in support was introduced in Windows Media Player 9 Series.
- Supports visualizations and Info Center View (Info Center View in WMP 9 Series and later) which displays media metadata fetched from the internet. Full screen visualizations are supported in WMP 9 Series and later.
- Windows Media Player 10 and later feature integration with a much larger number of online music stores and selecting a music store switches the Info Center view, radio and other online features to use services from that store. Purchased music from a particular store appears in a separate library node under the respective category.
- Features universal brightness, contrast, saturation and hue adjustments and pixel aspect ratio for all playable video formats.
- Since Windows Media Player 9 Series, the player supports crossfading, audio dynamic range (Quiet Mode) for WMA Pro and WMA Lossless, and auto volume leveling for certain media which includes volume level/gain information such as MP3 or Windows Media.
- Activates DVD and Blu-ray playback functionality with support for menus, titles and chapters, parental controls and audio track language selection if compatible decoders are installed. DVD playback features minus the necessary decoders were integrated into Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP. MPEG-2 and Dolby Digital (AC-3) decoders were included beginning with Windows Media Player 11 on Windows Vista (Home Premium and Ultimate editions only).
- Integrates web-browsing support to browse online music stores, shop for music and tune to internet radio stations since version 7.
- Supports extensive configurable privacy and security settings.
- Full keyboard-based operation is possible.
Features new to Windows Media Player 11
Windows Media Player 11 features many changes. The Media Library no longer presents the media items (such as albums and artists) in a tree-based listing. Rather, on selecting the category in the left panel, the contents will appear on the right, in a graphical manner with thumbnails featuring album art or other art depicting the item—a departure from textual presentation of information. The navigation pane can be customized for each library to show the user selected media or metadata categories. Missing album art can be added directly to the placeholders in the Library itself (though the program re-renders all album art imported this way into 1x1 pixel ratio, 200x200 resolution jpegs). There are separate Tiles, Icons, Details or Extended Tiles views for Music, Pictures, Video and Recorded TV which can be set individually from the navigation bar. Entries for Pictures and Video show their thumbnails. Windows Media Player 11 also includes the Windows Media Format 11 runtime which adds low bitrate support (below 128 kbit/s for WMA Pro), support for ripping music to WMA Pro 10 and updates the original WMA to version 9.2. Other features include:
- Instant Search - Searches and displays results as characters are being entered, without waiting for Enter key to be hit. Incremental search results are refined based on further characters that are typed.
- Improved synchronization features for loading content onto PlaysForSure-compatible portable players. WMP 11 supports reverse-synchronization, by which media present on the portable device can be replicated back to the PC.
- Support for ripping audio CDs to WAV and WMA 10 Pro formats.
- Media Sharing (via Windows Media Connect) allows content (Music, Pictures, Video) to be streamed to and from Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) AV enabled devices such as the PS3, Xbox 360, and Roku SoundBridge. This includes DRM protected PlaysForSure content. WMP 11 on Windows Vista can also connect to remote media libraries using this feature; this is not available on the Windows XP version.
- Disc spanning splits a burn list onto multiple discs in case the content does not fit on one disc.
- Portable devices appear in the navigation pane of the library where their content can be browsed and searched.
- Shuffle Sync to randomize content synced with the portable device, Multi PC Sync to synchronize portable device content across multiple PCs and Guest Sync to synchronize different content from multiple PCs with the portable device.
- The List pane includes an option to prompt the user to remove items skipped in a playlist upon save or skip them only during playback.
- CD Burning - CD Burning now shows a graphical bar showing how much space will be used on the disc.
- Stacking - Stacking allows graphical representations of how many albums there are in a specific category or folder. The pile appears larger as the category contains more albums.
- Global Status - Global status shows a broad overview of what the player is doing. The information presented includes status information regarding buffering, ripping, burning and synchronization.
Features new to Windows Media Player 12
Windows Media Player 12 is not available to operating systems earlier than Windows 7. It features broader built-in format support and comprehensive media streaming features.
Removed features
Version 11
- Auto sorting in the media library (similar to auto sorting in Windows Explorer) cannot be turned off.
- The ability to add media to the library for searching local or network files and selectively adding only new files or existing files has been removed. Media can only be added from monitored folders.
- The seek slider cannot be always shown when playing media. The mouse must be hovered over the progress bar above the playback controls to reveal the seek slider.
- The sort order is not preserved in the library like Windows Media Player 10 as long as the player is open.
- Next and Previous buttons to cycle through visualizations have been removed.
- Most Auto Playlists included by default in Windows Media Player 10 have been removed.
- Library options to configure what action to take when double clicking files (Add to List, Play All, Play Selected Items) have been removed.
- The total playlist time is no longer shown in the Now Playing list or in the Library without selecting items. It is only shown in the Library for selected items.[12] Total number of tracks is also only shown after selecting all tracks. The total size in MB is not shown in any view.[12]
- On Windows XP by default, Windows Media Connect 2.0 does not work after Windows Media Player 11 has been installed. Windows Media Player 11 includes the UPnP AV server for sharing media across the network which replaces similar functionality in Windows Media Connect, however it does not include the client, unlike Windows Media Connect.[13]
- On Windows Vista the ability to remove or reinstall Windows Media Player 11 has been removed, as it is integrated with the operating system. This forces users with bugs to either reinstall Vista or find help.
- The License Management tool available in prior versions of Windows Media Player has been removed since version 11. This prevents users of music download services from directly using Windows Media Player to back up their licenses and restore them to another computer. The user now must depend on the download service being able to assist with re-acquiring that license. Not all services support this so in some circumstances the user could lose the ability to play media which they've purchased for use with Windows Media Player 11. e.g. Walmart states: "Important Note: In many cases, we cannot replace song and license files if they are lost. We strongly suggest you back up your music by creating an audio CD or CDs using Windows Media Player 11" [14][15]
- It is not possible to change the media player's background to black. Instead, the background is a near-white shade of the color chosen in the color chooser.
- The Quick Access Panel, located next to the "Now Playing" tab in Windows Media Player 10 which enabled browsing the library via a pop-up/dropdown menu, has been removed. As a result of this, the library cannot be browsed through a menu and without having to switch to library view.
- In previous versions of Windows Media Player, the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl + I" could be used to capture the frame of video being displayed at the time the shortcut was initiated. This feature was removed for Windows Media Player 11.
- On Windows XP unlike previous Windows Media Player installers, Windows Media Player 11 tries to validate the copy of Windows as genuine. It will not install if the copy of Windows XP is not.
- The HighMAT burning capability integrated into Windows Media Player 10 is not available in Windows Media Player 11.
- The expandable tree view was removed from the navigation pane/left side of the media library.
- Display Anchor window when in skin mode option has been removed.
- Enable picture support for devices option has been removed.
- The Ambience, Particle, Plenoptic and Spikes visualizations have been removed.
Version 12
- The option to adjust the bit rate when burning data CDs has been removed.
- Mini-player was removed as also the ability to start the miniplayer for certain files based on specific text in their file names.
- The options to use the overlay mixer, video mixing renderer (VMR-7) or high quality mode (VMR-9) has been removed.
- Enhancements are only accessible from Now Playing view in a floating window and cannot be docked.
- Several player preferences are not saved and restored upon restarting the player. The playlist pane in Now Playing view is not shown automatically. Enhancements do not get restored when Windows Media Player is restarted. Even when manually restored, the previous position of the Now Playing window and enhancements is not retained.
- The context menu entry "Find In Library" which allowed locating the Now Playing song in the library was removed.
- Advanced Tag Editor, Color Chooser and Media Link for E-mail features have been removed.
Security issues
Microsoft Windows Media Runtime in Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows Server contained a coding error that permitted "remote code execution if a user opened a specially crafted media file". Such a file would allow the attacker to "then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights", if the account on which the file was played had administrator privileges.[16] The problem was addressed in a critical update issued on September 8, 2009.[17]
Other versions
Microsoft has also released versions of Windows Media Player for other platforms including Windows Mobile, Mac OS, Mac OS X, Palm-size PC, Handheld PC, and Solaris. Of these, only the Windows Mobile edition continues to be actively developed and supported by Microsoft. Version 1 of the Zune software was also based on Windows Media Player, later versions are not.
Windows Mobile
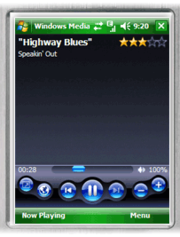
Windows Media Player for Pocket PC was first announced on January 6, 2000, and has been revised on a schedule roughly similar to that of the Windows version.[18] Currently known as "Media Player 10 Mobile", this edition (released in October 2004) closely resembles the capabilities of the Windows version of WMP 10, including playlist capabilities, a media library, album art, WMA Lossless playback, support for DRM-protected media, video playback at 640x480 with stereo sound, and the same Energy Blue interface aesthetics also seen in recent versions of Windows XP Media Center Edition. It also supports synchronization with the desktop version of WMP 10, and additionally supports synchronizing and transcoding of recorded television shows from Media Center. Media Player 10 Mobile is not available as a download from Microsoft; distribution is done solely through OEM partners, and is typically included on devices based on Windows Mobile.
Windows Mobile 6 includes a copy of Windows Media Player 10 Mobile, but with a similar (but not quite identical) theme as Windows Media Player 11.
Mac OS X
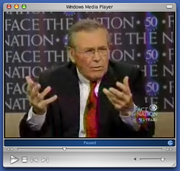
Version 9 was the final version of Windows Media Player to be released for Mac OS X before development was cancelled by Microsoft. Developed by the Windows Media team at Microsoft instead of the Macintosh Business Unit and released in 2003, on release the application lacked many basic features that were found in other media players such as Apple's iTunes and QuickTime. It also lacked support for many media formats that version 9 of the Windows counterpart supported on release 10 months earlier.
The Mac version supported only Windows Media encoded media (up to version 9) enclosed in the ASF format, lacking support for all other formats such as MP4, MPEG, and Microsoft's own AVI format. On the user interface front, it did not prevent screensavers from running during playback, it did not support file drag-and-drop, nor did it support playlists. While Windows Media Player 9 had added support for some files that use the WMV9 codec (also known as the WMV3 codec by the FourCC), in other aspects it was seen as having degraded in features from previous versions.
On January 12, 2006 Microsoft announced it had ceased development of Windows Media Player for Mac.[19] Microsoft now distributes a third-party plugin called WMV Player (produced and maintained by Flip4Mac) which allows some forms of Windows Media to be played within Apple's QuickTime player and other QuickTime-aware applications.[20]
Release history
| Version | Original release | Latest build | Operating system compatibility | Codename |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows | ||||
| Windows Media Player 12 | October 22, 2009 | 12.0.7600.16415 | Windows Server 2008 R2 Windows 7 |
|
| Windows Media Player 11 | October 30, 2006 | 11.0.6002.18111 (Vista) 11.0.5721.5268 (XP) |
Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista Windows XP SP2 & SP3 Windows XP x64 Edition |
Aurora (Vista) Polaris (XP) |
| Windows Media Player 10 | October 12, 2004 | 10.00.00.4074 | Windows Server 2003 SP2 Windows XP Windows XP x64 Edition |
Crescent [21] |
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | January 27, 2003 | 9.00.00.4507 (XP) 9.00.00.3364 (2000) 9.00.00.2991 (Server 2003) |
Windows XP Windows Me Windows 2000 Windows 98 SE |
Corona |
| Windows Media Player for Windows XP (Version 8) |
October 25, 2001 | 8.0.0.4477 | Windows XP | |
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 16, 2001 | 7.1 | Windows Me Windows 2000 Windows 98 |
|
| Windows Media Player 7.0 | July 17, 2000 (2000 and 98)[22] September 14, 2000 (Me) |
7.0 | Windows Me Windows 2000 Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.4 ( mplayer2 for XP and 2000) |
November 22, 1999 | 6.4.09.1130 (XP) 6.4.09.1129 (2000) 6.4.09.1125 (Server 2003) |
Windows XP Windows Me Windows 2000 Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.1 | June 25, 1998 | Windows 98 Windows 95 |
||
| Windows CE/Windows Mobile | ||||
| Windows Media Player 10.3 Mobile | February 12, 2007 (6) | Windows Mobile 6.1 Windows Mobile 6 Windows Mobile 5 |
||
| Windows Media Player 10.2 Mobile | Windows Mobile 5.0 | |||
| Windows Media Player 10.1 Mobile | May 10, 2005 | Windows Mobile 5.0 | ||
| Windows Media Player 10 Mobile | October 12, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | ||
| Windows Media Player 9.0.1 | March 24, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | ||
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | June 23, 2003 | Windows Mobile 2003 | Corona | |
| Windows Media Player 8.5 | October 11, 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | ||
| Windows Media Player 8.01 | July 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | ||
| Windows Media Player 8 | October 4, 2001 (Pocket PC) December 5, 2001 (Smartphone) |
Pocket PC 2002 Smartphone 2002 |
||
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 21, 2001 | Pocket PC 2000 | ||
| Windows Media Player 7 | December 12, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | ||
| Windows Media Player 1.2 | September 7, 2000 | Handheld PC 2000 | ||
| Windows Media Player 1.1 | Palm-size PC CE 2.11 | |||
| Windows Media Player | April 19, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | ||
| Mac | ||||
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | November 7, 2003 | Mac OS X | Corona | |
| Windows Media Player 7 | July 24, 2001 | 7.0.1 | Mac OS 9 Mac OS 8 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | Mac OS 8 Mac OS 7 |
||
| Solaris | ||||
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | Solaris | ||
European Commission case
In March 2004, the European Commission in the European Union Microsoft antitrust case fined Microsoft €497 million and ordered the company to provide a version of Windows without Windows Media Player, claiming Microsoft "broke European Union competition law by leveraging its near monopoly in the market for PC operating systems onto the markets for work group server operating systems and for media players". The company has made available a compliant version of its flagship operating system under the negotiated name "Windows XP N", though the product has not been very successful.[23] Windows Vista and Windows 7 are also available in "N" editions. Still, with these editions it is possible to either install Windows Media Player (XP/Vista)[24] or the Media Restore Pack through Windows Update (Vista) to gain the media player functionality back and forth.
See also
- List of media players
- Comparison of video player software
- Media Transfer Protocol
- Windows Media Encoder
- Windows Media Services
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Except for "N" and "KN" editions of Windows XP and Windows Vista.
- ↑ Except for "N" editions of Windows 7.
- ↑ Windows 7 Has Been Released to Manufacturing
- ↑ http://www.microsoft.com/windows/windows-7/features/windows-media-player-12.aspx
- ↑ "Windows Version History (MSKB32905)". Knowledge Base. Microsoft. July 19, 2009. http://support.microsoft.com/kb/32905. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ↑ "Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions". Toasty Tech. http://toastytech.com/guis/win3mme.html. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ↑ "Video for Windows". PC Tech Guide. http://www.pctechguide.com/45DigitalVideo_Video_for_Windows.htm. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ↑ http://www.jmcgowan.com/avitech.html
- ↑ "DirectShow: Core Media Technology in Windows XP Empowers You to Create Custom Audio/Video Processing Components". MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. July 2002. http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/cc301631.aspx. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ↑ DSP Plug-in Packaging: MSDN
- ↑ Windows Media Player 10 additional documentation
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Windows Media Player 11 FAQs
- ↑ Windows Media Connect Practical Overview
- ↑ "Walmart.com - Music Downloads". Walmart. January 2008. http://musicdownloads.walmart.com/catalog/servlet/HelpTopicServlet?topicIndex=0#5. Retrieved 2007-01-23.
- ↑ "Backing up and restoring licenses". Microsoft. November 2006. http://www.microsoft.com/windows/windowsmedia/player/11/readme.aspx#1608319. Retrieved 2007-01-04.
- ↑ "Microsoft Security Bulletin MS09-047: Critical Vulnerabilities in Windows Media Format Could Allow Remote Code Execution". Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. 8 September 2009. http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/bulletin/MS09-047.mspx.
- ↑ "MS09-047: Description of the security update for Windows Media Format Runtime, Windows Media Services, and Media Foundation: September 8, 2009". Microsoft Support. Microsoft. 10 September 2009. http://support.microsoft.com/kb/968816.
- ↑ "Microsoft Unveils Windows Media Player for Palm-Size and Pocket PCs". Microsoft PressPass. Microsoft. January 6, 2000. http://www.microsoft.com/Presspass/press/2000/jan00/palmpocketpr.mspx. Retrieved 2006-05-14.
- ↑ Fried, Ina (2006-01-12). "Music stops for Mac Windows Media Player". CNET. http://news.com.com/Music+stops+for+Mac+Windows+Media+Player/2100-1047_3-6026715.html?part=rss&tag=6026715&subj=news. Retrieved 2006-12-21.
- ↑ "Windows Media Components for QuickTime". Microsoft. http://www.microsoft.com/windows/windowsmedia/player/flip4mac.mspx. Retrieved 2007-03-30.
- ↑ Media Transfer Protocol presentation
- ↑ http://www.microsoft.com/presspass/press/2000/Jul00/WMP7PR.mspx
- ↑ Marson, Ingrid (2005-11-18). "Still 'no demand' for media-player-free Windows". CNET. http://news.com.com/Still+no+demand+for+media-player-free+Windows/2100-1016_3-5960750.html. Retrieved 2006-12-21.
- ↑ Microsoft. Download Center. "be used to restore Windows Media Player and related technologies to N and KN editions of Windows Vista." Retrieved 2008-07-26
External links
- Microsoft Windows Media home page
- A Little Windows Media Player History
- Microsoft ports Windows Media to Linux (10 April 2003, vnunet.com)
- Error Messages in Windows Media Player 10
- Error Messages in Windows Media Player 9
- List of default codecs in Windows XP SP2 and WMP 9 and 10
- Windows Media Player for Mac
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||